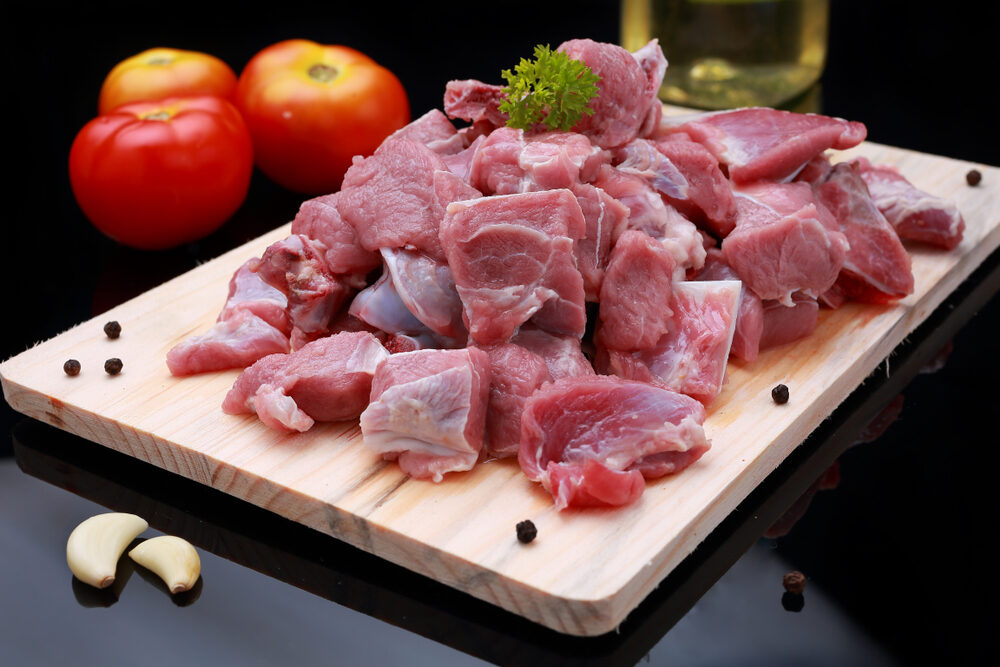
Mutton, which refers to the meat of mature sheep, is a rich source of nutrients and has been a dietary staple in many cultures for centuries. Known for its distinctive flavor and versatility in culinary applications, mutton offers several health benefits. This article delves into the nutritional profile of mutton and the advantages of incorporating it into your diet.
Nutritional Information (per 100 grams of cooked mutton)hy
- Calories: 250 kcal
- Protein: 25 grams
- Total Fat: 16 grams
- Saturated Fat: 7 grams
- Monounsaturated Fat: 6 grams
- Polyunsaturated Fat: 1 gram
- Cholesterol: 80 mg
- Carbohydrates: 0 grams
- Vitamin B12: 2.6 mcg (43% of the Daily Value)
- Iron: 2.1 mg (12% of the Daily Value)
- Zinc: 4.6 mg (31% of the Daily Value)
- Selenium: 27.6 mcg (40% of the Daily Value)
- Phosphorus: 200 mg (20% of the Daily Value)
- Niacin (Vitamin B3): 6.8 mg (34% of the Daily Value)
Health Benefits of Mutton
- High-Quality Protein:
- Mutton is an excellent source of high-quality protein, essential for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting overall growth and development. Protein is crucial for maintaining muscle mass, especially in older adults.
- Rich in Vitamins and Minerals:
- Mutton is packed with essential vitamins and minerals. It is particularly high in vitamin B12, which is important for nerve function and the production of DNA and red blood cells. The meat is also a good source of niacin, zinc, iron, and phosphorus, all of which play critical roles in various bodily functions.
- Supports Immune Function:
- Zinc, found abundantly in mutton, is vital for a healthy immune system. It aids in cell division, cell growth, wound healing, and the breakdown of carbohydrates.
- Improves Bone Health:
- Phosphorus and selenium in mutton contribute to stronger bones. Phosphorus is crucial for the formation of bones and teeth, while selenium helps prevent oxidative damage to cells and tissues.
- Boosts Energy Levels:
- The B vitamins in mutton, particularly niacin and vitamin B12, are essential for converting food into energy. They help in the metabolic processes that turn nutrients into energy, thereby preventing fatigue and boosting overall energy levels.
- Supports Brain Health:
- Vitamin B12 is critical for brain health and cognitive function. Adequate B12 intake can help prevent memory loss and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Heart Health:
- While mutton does contain saturated fats, it also has monounsaturated fats, which are beneficial for heart health. Monounsaturated fats can help reduce bad cholesterol levels in the blood, lowering the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Potential Considerations
- High in Saturated Fat:
- Mutton contains a significant amount of saturated fat, which can contribute to elevated cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease if consumed in excess. It is important to balance mutton consumption with other lean proteins and maintain a diet low in saturated fats.
- Caloric Content:
- Mutton is relatively high in calories compared to other lean meats. Those monitoring their caloric intake should consume mutton in moderation to avoid excessive calorie consumption.
- Purine Content:
- Mutton is high in purines, which can increase uric acid levels in the body and may exacerbate conditions such as gout in susceptible individuals.
Conclusion
Mutton is a nutrient-dense meat that offers numerous health benefits, including high-quality protein, essential vitamins, and minerals. It supports muscle growth, immune function, bone health, and brain health, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet. However, due to its saturated fat content, it should be consumed in moderation as part of a varied and balanced diet. Incorporating mutton into your meals can provide a flavorful and nutritious option that contributes to overall well-being.