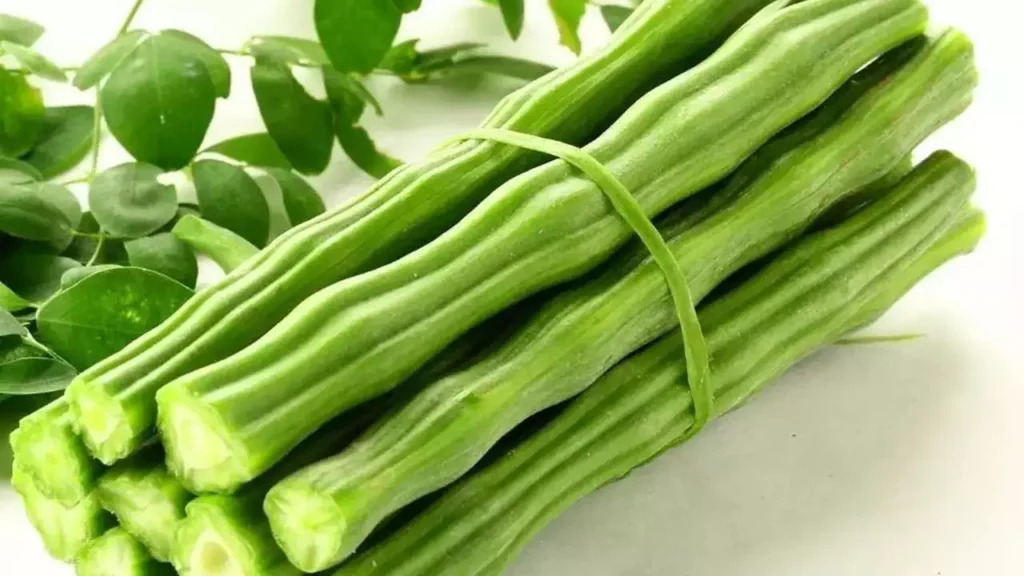
Drumsticks, derived from the Moringa oleifera tree, are esteemed in traditional medicine and culinary practices for their rich nutritional content and health-promoting properties.
🥦 Nutritional Profile (Per 100g of Raw Drumstick Pods)
- Calories: 64 kcal
- Protein: 9.4 g
- Carbohydrates: 8.28 g
- Dietary Fiber: 2.0 g
- Fat: 1.4 g
- Vitamins: Rich in Vitamin A, Vitamin C, and Vitamin B6
- Minerals: Contains Calcium, Iron, Magnesium, and Potassium
Additionally, Moringa leaves are notable for their high content of essential amino acids and bioactive compounds, including flavonoids and phenolic acids, contributing to their antioxidant properties.
🌿 Health Benefits of Drumsticks
1. Supports Immune Function
The high Vitamin C content in drumsticks enhances immune system efficiency, aiding in the prevention of common infections.
2. Regulates Blood Sugar Levels
Compounds in Moringa have been observed to assist in maintaining healthy blood glucose levels, which is beneficial for individuals managing diabetes.
3. Promotes Bone Health
Drumsticks are a good source of calcium and iron, essential minerals that contribute to bone strength and density.
4. Enhances Digestive Health
The dietary fiber in drumsticks aids in digestion and helps prevent constipation by promoting regular bowel movements.
5. Possesses Anti-inflammatory Properties
Bioactive compounds in Moringa exhibit anti-inflammatory effects, which may help reduce inflammation in the body.
6. Supports Cardiovascular Health
Regular consumption of drumsticks may contribute to heart health by helping to manage cholesterol levels and blood pressure.
7. Protects Liver Function
Moringa has been studied for its potential to protect the liver against damage due to its antioxidant properties.
8. Aids in Blood Purification
The detoxifying properties of drumsticks assist in purifying the blood, which can enhance overall health.
🍽️ Incorporating Drumsticks into Your Diet
- Culinary Uses: Drumsticks can be added to soups, stews, and curries for enhanced flavor and nutrition.
- Moringa Leaves: The leaves can be used in salads, smoothies, or dried and powdered for use in teas and supplements.
⚠️ Precautions
- Pregnancy: Pregnant women should consult healthcare providers before consuming Moringa, as certain parts of the plant may not be advisable during pregnancy.
- Medication Interactions: Moringa may interact with medications for diabetes, blood pressure, and thyroid disorders. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional before adding it to your regimen.